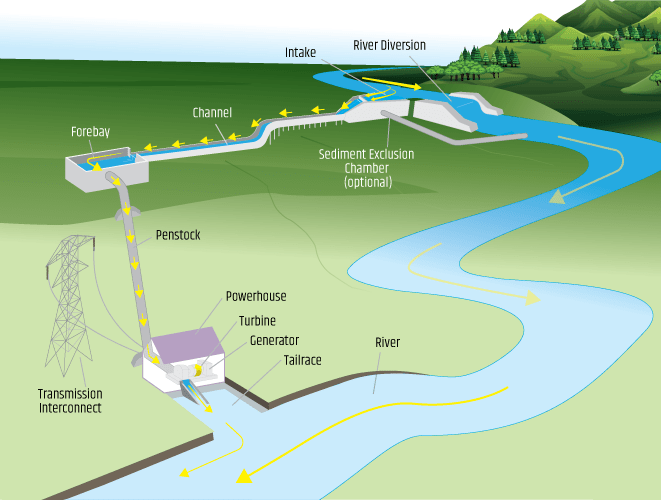
The registration process for hydropower projects in Nepal as of 2024
The registration process for hydropower projects in Nepal as of 2024 involves several steps typically outlined by the Department of Electricity Development (DoED). With its vast water resources and significant hydropower potential, Nepal offers numerous opportunities for investment in hydropower projects. While bureaucratically intensive, the registration and development process is structured to ensure sustainable development and efficient utilization of resources. Below is a comprehensive guide on the process, requirements, and opportunities related to hydropower registration in Nepal.
Process for Hydropower Registration
- Preliminary Study and Planning
- Site Identification: Conduct a feasibility study to identify potential sites for hydropower projects. This involves hydrological, geological, and environmental assessments.
- Initial Environmental Examination (IEE): An IEE or Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) may be required depending on the project size.
- Registration with the Department of Electricity Development (DoED)
- License Application: Apply for a survey license to the DoED. The application should include a detailed project proposal, feasibility study report, and environmental study reports.
- Approval and License Issuance: The DoED reviews the application and, if satisfactory, issues a survey license, which allows for detailed project planning and resource assessment.
- Detailed Project Report (DPR) Preparation
- Technical Studies: Conduct detailed technical, environmental, and social studies to prepare a comprehensive DPR.
- Power Purchase Agreement (PPA): Negotiate and sign a PPA with the Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA) or other power purchasers. For projects up to 10 MW, secure a PPA with the Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA), which has been made more accessible for small investors.
- Construction License Application
- Submit DPR: Submit the DPR and an application for a construction license to the DoED.
- Review and Approval: The DoED reviews the DPR and, if found satisfactory, issues a construction license.
- Project Implementation and Monitoring
- Construction: Begin construction as per the approved DPR, adhering to environmental and social management plans.
- Monitoring: The DoED and other relevant authorities monitor projects regularly to ensure compliance with project specifications and regulatory requirements.

Requirements for Hydropower Registration
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance
- Company Registration: Register the project company under Nepalese law.
- Survey and Construction Licenses: Obtain the necessary survey and construction licenses from the DoED.
- Environmental Clearances: Obtain necessary environmental clearances based on the IEE or EIA reports.
- Technical Documentation
- Feasibility Study Report: Detailed hydrological, geological, and technical studies.
- DPR: Comprehensive DPR including technical, financial, and environmental aspects.
- PPA: Signed PPA with power purchasers.
- Financial Requirements
- Project Financing: Secure financing for the project through equity, loans, or a combination of both.
- Financial Plan: A detailed financial plan demonstrating project viability and sustainability.
Opportunities in Hydropower Development
- Abundant Water Resources
- Nepal has an estimated hydropower potential of around 83,000 MW, with 42,000 MW considered economically feasible.
- Government Incentives
- The Nepalese government offers various incentives for hydropower development, including tax holidays, concessional loans, and subsidies for rural electrification projects.
- Growing Energy Demand
- Increasing domestic demand for electricity and the potential for export to neighboring countries like India and China present significant market opportunities.
- Investment Opportunities
- Both foreign and domestic investors can invest in hydropower projects independently or through public-private partnerships (PPPs).
- Green Energy Initiatives
- Hydropower development aligns with global green energy initiatives, offering opportunities for carbon credits and international funding from organizations supporting renewable energy projects.
Conclusion
Given the country’s vast water resources and supportive regulatory framework, hydropower development in Nepal presents a lucrative opportunity for investors. By adhering to the detailed registration process and fulfilling all regulatory requirements, developers can capitalize on the growing energy demand and contribute to Nepal’s sustainable development goals.
